This engineering guide explains water treatment chemical dosing from raw water to membranes and boilers—what each chemical does, where to inject it, how to size it, and how to avoid unsafe or ineffective combinations. It is written for B2B plants (RO/UF/EDI, industrial & municipal) and includes quick tables, formulas, safety notes, and a purchasing checklist.
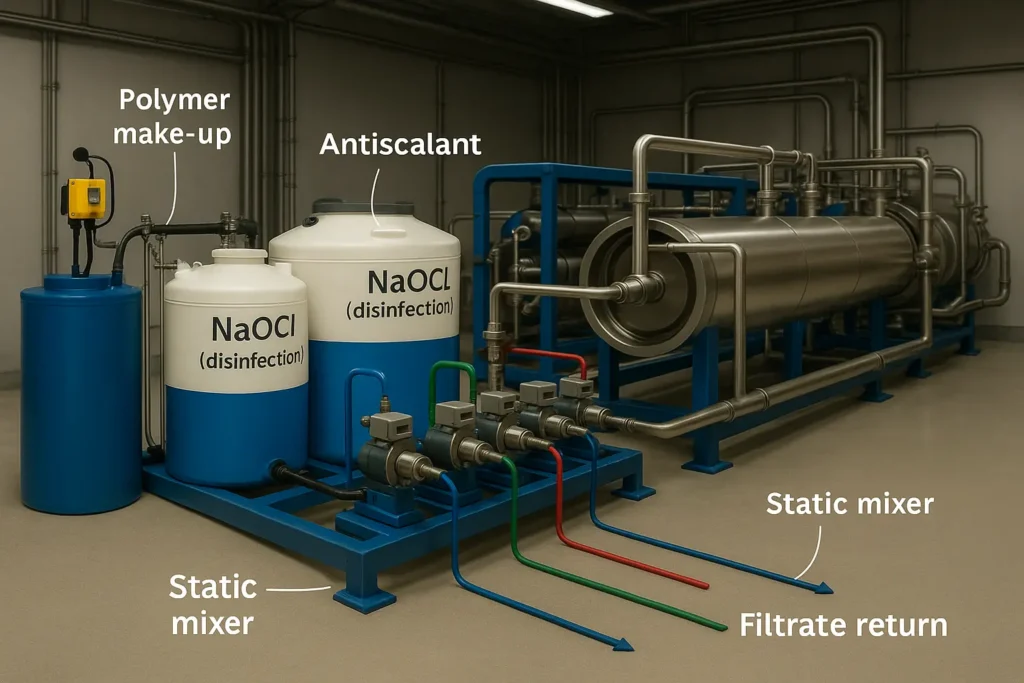

This water treatment chemical dosing guide is written for engineers who need fast, reliable decisions on chemicals and injection points.
Water Treatment Chemical Dosing Overview (Snapshot)
| Stage | Typical chemicals | Main objective | Key controls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw water / intake | Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) | Disinfection / biofouling control | Free chlorine & contact time; materials compatibility |
| Coagulation / clarification | Inorganic coagulants; cationic/anionic polymers | Rapid solid–liquid separation | pH, mixing energy, aging, injection point |
| UF backwash & CIP | NaOH, HCl, NaOCl (as allowed by membrane) | Remove organic/inorganic foulants; sanitize | Chemical sequence & concentration; strict compatibility |
| RO feed | Antiscalant; sodium bisulfite (SBS) for dechlorination; optional NaOH for pH | Scale control; protect PA membranes from oxidants; improve specific removals | LSI/CSI, recovery, free Cl₂ < 0.05 mg/L, reaction time & mixing |
| Granular activated carbon (GAC) | - | Remove residual chlorine & organics | Backwash regime; prevent carbon fines downstream |
| Boiler water | Amine for pH; oxygen scavenger; phosphate | Minimize corrosion & scale in steam systems | DO, alkalinity, phosphate balance, conductivity |
Use this water treatment chemical dosing overview to align objectives, dosing points and controls across your plant.
Raw water disinfection with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)
NaOCl forms hypochlorous acid (HOCl), a strong oxidant for bacteria, algae and biofilm control at intake or equalization tanks. Maintain the required free chlorine and contact time; verify downstream compatibility (GAC or SBS dechlorination before RO).
- Do not mix acids with hypochlorite—this can release chlorine gas.
- Keep dosing skid and storage segregated; protect from heat and sunlight to limit decomposition.
- Record residual chlorine and tank turnover; design for secondary containment.

Coagulation & flocculation
Coagulation neutralizes charges on colloids; polymers bridge particles into settleable flocs. Optimize by jar testing and then control pH, mixing energy (rapid mix → flocculation), polymer aging time, and the exact injection point relative to mixers and clarifiers/filters.
- Start with low polymer concentration (e.g., 0.1–0.3%) and increase by response.
- Monitor turbidity and SDI leaving multimedia filters to protect downstream UF/RO.
UF Cleaning & Water Treatment Chemical Dosing
UF membranes typically combine alkaline cleaning for organics/biofilm, an acid step for inorganic scale (e.g., CaCO₃, Fe), and—if permitted—an oxidative sanitation step. Choose the sequence based on foulant diagnosis; never mix hypochlorite with acids.Effective water treatment chemical dosing on UF membranes requires the right sequence and safe compatibility.
- Set backwash intervals by flux decline and trans-membrane pressure (TMP) trends.
- For offline CIP, isolate, soak, recirculate, then slow flush to neutral pH and conductivity.
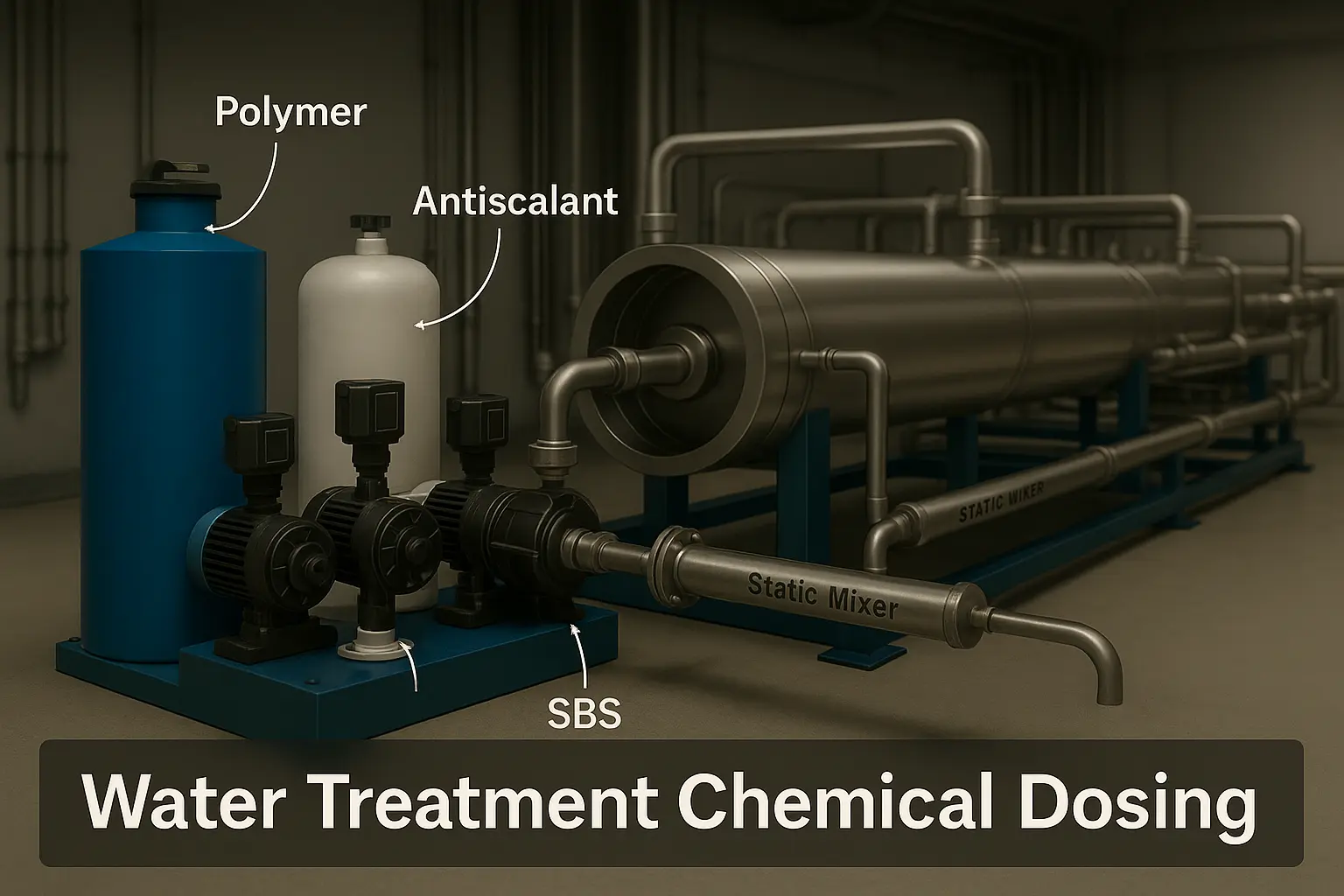
RO Water Treatment Chemical Dosing
RO water treatment chemical dosing focuses on dechlorination and antiscalant control with verified residence time.
5.1 Dechlorination with sodium bisulfite (SBS)
Polyamide RO membranes are chlorine-sensitive. Reduce free Cl₂ to < 0.05 mg/L قبل the first element. Provide adequate mixing (static mixer) and reaction time.
Quick sizing: For every 1.0 mg/L of free chlorine, dose ≈ 1.8–3.0 mg/L of SBS (includes safety factor).
Stoichiometry: 1.47 mg/L SBS per 1.0 mg/L Cl₂ (theoretical).
Good practice: 20–30 seconds of pipe residence after injection, then verify residual Cl₂ = non-detect.
5.2 Antiscalant (and SHMP notes)
Use modern antiscalants matched to your water chemistry and recovery. Historic SHMP (sodium hexametaphosphate) can hydrolyze during storage and may promote calcium phosphate scale; use only when specified and refresh solutions frequently.
- Confirm scaling indices (LSI/CSI), sulfate/silica limits and recovery targets in design software.
- Coordinate with acid dosing if needed to widen the scaling window.
5.3 pH adjustment & special cases
Raising pH with NaOH before high-pH RO (e.g., two-pass RO/HERO) improves removal of weak acids such as CO₂, silica and boron. Higher pH increases LSI and can precipitate CaCO₃/Fe/Mn—use softening/iron removal or pre-acidification as needed.
5.4 Granular activated carbon (GAC)
GAC protects RO by removing residual oxidants and organics. Backwash sufficiently and flush new carbon to avoid fines and microbial growth. Keep records of differential pressure and backwash flow.
Boiler Water Treatment Chemical Dosing
Steam systems use a different chemistry toolkit: alkalizers (amines) to raise pH and minimize carbonic acid corrosion, oxygen scavengers (e.g., hydrazine or alternatives) to reduce DO, and phosphates to control precipitation regimes in the drum. Track DO, alkalinity, phosphate balance, iron/copper and conductivity at defined sampling points.
Safety & chemical compatibility
- Never combine acids with hypochlorite (risk of chlorine gas).
- Separate oxidants from reducers (NaOCl vs. SBS) by dedicated lines and isolation valves.
- Use compatible materials (SS304/316L, UPVC, PTFE). Provide secondary containment and eyewash/shower nearby.
- Label tanks and day-tanks; implement interlocks for overfeed/low-level alarms.
Further reading: Water Environment Federation resources و EPA water research.
Plan water treatment chemical dosing storage and segregation to prevent oxidant–reducer contact.
Dosing & preparation essentials
- Solution stability: Refresh SBS and SHMP frequently; store sealed, cool, and out of direct light.
- Backup logic: Use flow-paced dosing with manual trim; add residual analyzers where practical (Cl₂, ORP, pH).
- Injection points: Place upstream of mixers with verified residence (RO dechlorination ≥ 20–30 s).
Verification checklist
- Raw water: free Cl₂ within spec; contact time achieved.
- Coagulation: jar-test curve documented; turbidity/SDI targets met.
- UF: flux/TMP baseline trended; CIP sequence validated; final rinse to neutral.
- RO: free Cl₂ non-detect; SBS reaction time verified; antiscalant window OK; pH/recovery consistent.
- GAC: backwash schedule and ΔP logs complete.
- Boiler: DO/pH/phosphate/conductivity within limits; corrosion indicators checked.

Common mistakes & fast fixes
- RO membrane oxidation: dechlorination inadequate → increase SBS, check static mixer and residence, re-test Cl₂.
- UF cleaning ineffective: wrong foulant diagnosis → swap acid/caustic order or concentration; extend soak.
- Carbon fines into RO: insufficient new-media flush/backwash → extend backwash and add strainer.
- Boiler scaling: phosphate/alkalinity imbalance → adjust dosing and blowdown; verify test kits.
الأسئلة الشائعة
Why dose sodium bisulfite before RO?
Polyamide RO membranes are vulnerable to oxidants. SBS reduces free chlorine to protect the membrane; provide mixing time and verify non-detect residual before the first element.
Can SHMP be used as an antiscalant?
It can in legacy systems, but it hydrolyzes in storage and can form calcium phosphate scale. Modern antiscalants are preferred for stable, predictable performance.
How do I decide acid-first or caustic-first for UF/RO cleaning?
Choose by foulant type: carbonate/metal scales → acid-first; organic/biofoulants → caustic-first. Always follow the membrane OEM limits.
When should pH be raised before RO?
In two-pass or high-pH RO (HERO) to improve removal of CO₂, silica and boron—while controlling calcium carbonate and iron/manganese precipitation risks.
Next steps: get a dosing plan for your plant
Upload your water analysis (flow, pH, alkalinity, free Cl₂, SDI/turbidity, recovery, silica/boron, boiler parameters) and we’ll return a dosing proposal and a BOM draft within 24 hours. Request a review →
Related reading and parts: RO system overview, UF membrane guide, dosing pumps & accessories, stainless steel tanks & manifolds.
Stark Water Engineering Team — process design, commissioning & troubleshooting