This practical guide explains the reverse osmosis system working principle, how each module fits into the train, and how to operate, maintain and troubleshoot RO skids with confidence. You’ll get checklists, schedules, diagrams and FAQs that shorten commissioning and reduce downtime.
1) Reverse Osmosis System Working Principle — What an RO System Is & Where It Fits
A reverse osmosis (RO) system uses a semi-permeable membrane to separate water from dissolved salts and organics. In a typical plant the process train is Pretreatment → RO purification → Post-treatment. Compared with ion exchange, a modern RO system provides high desalting efficiency with lower chemical footprint and minimal regeneration waste. RO is also the core desalting step before polishing processes such as EDI, mixed bed or UV-TOC.
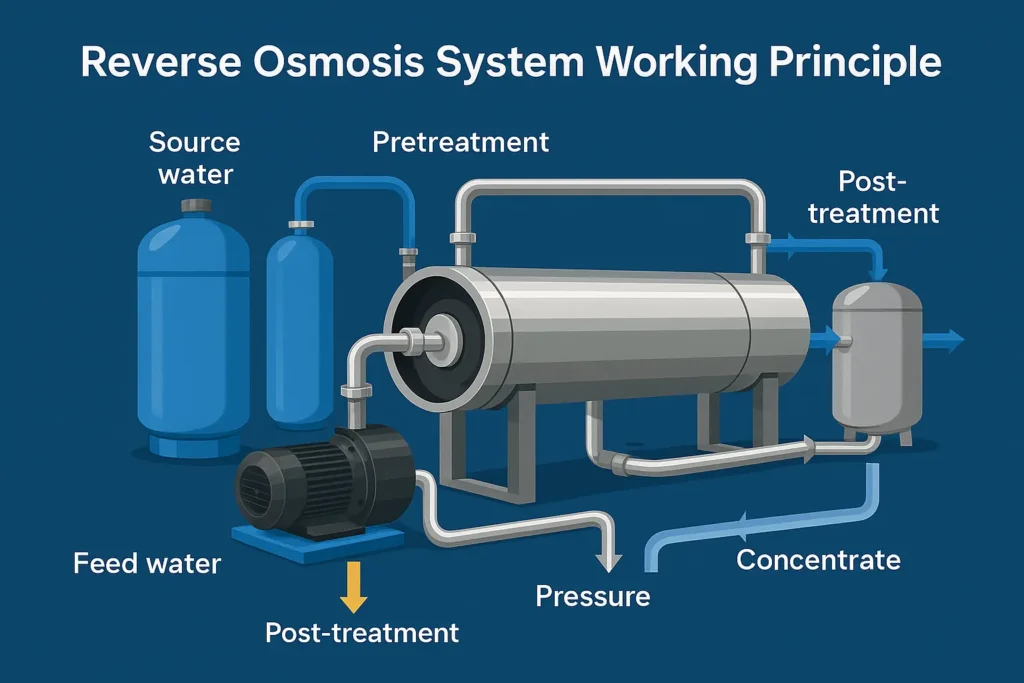
In practice, the reverse osmosis system working principle anchors the core desalting step between pretreatment and post-treatment.
2) Reverse Osmosis System Working Principle — How It Works
Osmosis drives water across a membrane from low to high solute concentration. A reverse osmosis system working principle applies pressure higher than the osmotic pressure on the feed side so water molecules permeate while most ions and organics are rejected. Composite polyamide membranes typically achieve ≥98% nominal salt rejection under design conditions.
- Two streams: 透過液 (product) and Concentrate (reject). Instrument the skid with feed/permeate/concentrate pressure, ΔP, flows, conductivity, temperature, pH/ORP (where relevant).
- Factors that affect salt passage: temperature, pressure, pH/CO2, concentration polarization, membrane age and biofouling.
- よくある落とし穴: ignoring dissolved CO2 when evaluating conductivity; inadequate dechlorination that oxidizes polyamide; overshooting recovery leading to scaling.
3) Reverse Osmosis System Working Principle — Components & Pretreatment
Pretreatment: MMF / GAC / Softener / Cartridge
| Unit | Primary function | Engineer’s notes |
|---|---|---|
| Multimedia filter (MMF) | Remove suspended solids/colloids; reduce turbidity/SDI. | Backwash & air scour as scheduled; target SDI ≤ 3 for stable operation. |
| Activated carbon (GAC) | Dechlorination; adsorb organics/odor; color reduction. | Verify free Cl2=ND before RO; watch for carbon fines and biological growth. |
| Softener (cation resin) | Exchange Ca/Mg to Na to control hardness scaling. | Set proper brine salinity, flow and contact time; regenerate by time/volume. |
| Cartridge filter (e.g., 5 µm) | Guard against media carryover and last-chance particulates. | Change on ΔP rise or time; verify seals and housings are clean and sanitary. |
RO skid & post-treatment
- RO skid: high-pressure pump, pressure vessels & membranes, manifolds/valves, instruments and automation.
- 治療後: depending on spec, add EDI or mixed bed, UV-TOC, fine carbon and stainless-steel storage/distribution (304/316L; hygienic where required).
4) Reverse Osmosis Maintenance — Protecting the Reverse Osmosis System Working Principle
Good data and gentle handling are the backbone of reverse osmosis maintenance. Keep a daily log, flush on shutdowns and control oxidants strictly. Follow OEM chemical limits and safety procedures.

Daily log — suggested tags
- Feed/permeate/concentrate pressure & ΔP
- Flows (feed/permeate/concentrate)
- Conductivity (feed/permeate)
- Temperature
- pH/ORP & free chlorine upstream of RO
- Recovery setpoint and alarms
Sanitation & flushing
- Permeate flush on shutdown; periodic chemical/thermal sanitation where hygienic service is required.
- Validate CIP sequence and final neutral rinse; record post-CIP baseline.
Dechlorination & safety
- Use GAC or sodium bisulfite (SBS) to ensure free Cl2=ND at RO inlet; confirm with on-site test kits.
- Depressurize and lock out pumps before opening housings; follow vessel OEM instructions for end-cap handling.
5) RO Consumables & Replacement Schedule
Actual life depends on feed quality, temperature, flux and housekeeping. Use the table below as a starting window and verify on site.
| 消耗品 | Typical interval | What governs life |
|---|---|---|
| Quartz sand (MMF media) | 10–24 months | Fines loss, headloss growth, backwash performance |
| Activated carbon (GAC) | 10–12 months | Breakthrough, pressure loss, biological growth risk |
| Softener resin | 10–12 months; regenerate every 1–3 days | Leakage/hardness spike, REG salt quality, iron fouling |
| 5 µm PP cartridge | 3–6 months (or ΔP trigger) | SDI/turbidity spikes, carbon fines |
| RO膜 | ~12 months design life (often 24–36 months in good service) | Scaling/biofouling, oxidant exposure, cleaning practice |
6) Reverse Osmosis Troubleshooting & Emergency Actions
Fast triage symptom map
| Symptom | Likely root causes | First checks |
|---|---|---|
| Permeate conductivity rises | Membrane oxidation, CO2 effect, channeling, temperature change, O-ring leaks | Free Cl2 test, feed/permeate temp, stage conductivity profile, inspect O-rings/end-caps |
| ΔP increases | Particulate fouling, biofouling, wrong/failed cartridges, scale | Check cartridge ΔP, particle counts/SDI, confirm antiscalant window, schedule CIP |
| Permeate flow drops | Fouling/scaling, pump curve off, VFD setpoint drift, instrument error | Normalize flow to temperature, verify pressure & recovery control, calibrate instruments |
| Leak/rupture | Seal failure, over-pressure, improper end-cap handling | Stop feed & power, depressurize safely, contain spill, follow OEM repair protocol |
Emergency actions
- Major leak or unsafe condition → Shut feed & power, depressurize, lock-out, notify maintenance.
- Membrane/HP pump failure → If process allows, bypass with softened water to maintain supply.
- Analyzer out of spec → Cross-check with handheld meters; if in doubt, run conservative setpoints and sample to lab.
7) Reverse Osmosis System Working Principle — Design Notes
- Flux & recovery: match to feed SDI/temperature; excessive recovery accelerates scaling and ΔP rise.
- CO2 & conductivity: dissolved carbon dioxide passes RO and inflates permeate conductivity—address via degassing or downstream polishing when specs are tight.
- Dechlorination: GAC or SBS redundancy is cheap insurance for PA membranes.
8) Applications & Industry Use Cases
Boiler make-up, micro-electronics/UPW, beverage blending water, pharma PW/HPW/WFI pretreatment, municipal drinking water polishing, chemical and electroplating reuse, and seawater desalination pre/post-treatment are all common scenarios for a reverse osmosis system working principle in practice.

9) Reverse Osmosis Maintenance Checklists (downloadable)
毎日
- Record P/ΔP/flows/cond/temp; confirm recovery setpoint & alarms.
- Verify free Cl2=ND before RO; check cartridge ΔP trend.
- Permeate flush after short stops; housekeeping around pumps & drains.
ウィークリー
- Calibrate key analyzers (conductivity, pH/ORP); inspect end-caps & O-rings.
- Review SDI/turbidity logs; confirm backwash and softener regeneration records.
Monthly
- Normalize permeate flow; compare to acceptance baseline.
- Audit chemical inventories (SBS/antiscalant/cleaners); check safety showers/eyewash.
10) FAQs
What damages RO membranes most quickly?
Free chlorine/oxidants, high recovery scaling, and long stagnant periods with poor sanitation. Control oxidants upstream and run within the antiscalant window.
How often should I replace the 5 µm cartridge?
Use ΔP and time. Typical interval is 3–6 months; shorten during SDI/turbidity spikes or after new carbon commissioning.
Can I run a bypass when the RO fails?
Where process risk allows, temporary softened water bypass maintains supply while repairs are made. Clearly label and trend any spec impacts.
What is a safe free-chlorine level before RO?
Non-detect at the RO inlet. Verify with handheld kits even if you have online ORP/Cl2 analyzers.
Why does permeate conductivity rise after shutdown?
Temperature changes, CO2 absorption and concentration polarization can shift readings. Flush and re-stabilize before judging membrane health.
11) Next steps
Send us your feed analysis, target conductivity/TOC and footprint/energy constraints. We’ll return a preliminary PFD + BOM + set points within 48 hours. Request a review →
Related pages: RO system overview - Reverse osmosis troubleshooting - Double pass reverse osmosis - UF membrane guide.
Further reading: US EPA – Water Research; Water Environment Federation – Publications.
スターク・ウォーター・エンジニアリング・チーム — Process design, commissioning & troubleshooting

