Reverse osmosis, also known as reverse osmosis, is a membrane separation operation that uses pressure difference as a driving force to separate solvents from solutions. Because it is in the opposite direction of natural osmosis, it is called reverse osmosis.
Specifically, The water production rate decays rapidly, and the operating pressure and pressure difference increase rapidly.
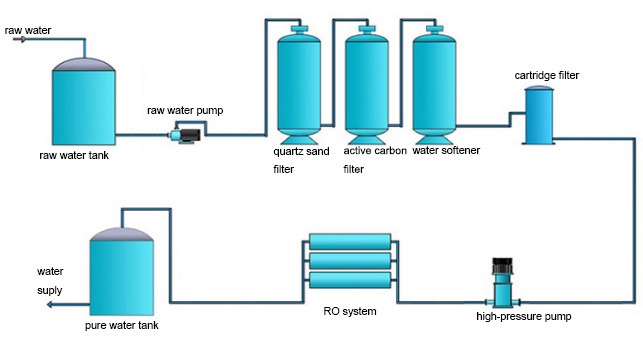
Due to the deterioration of the performance of the pretreatment equipment, the turbidity, SDI value, COD value, etc. of the effluent seriously exceed the requirements of the inlet water quality.
Specific manifestations include:
CMF or UF membrane filament breakage; serious bacterial and microbial growth in the buffer water tank; chaotic layer or biased flow of the filter media in the multi-media filter; and powderization or serious microbial growth in the activated carbon filter.


