RO antiscalant vs cooling water antiscalant: here’s how they differ in chemistry, purity, dosing and acceptance—so you never cross-use the wrong product.
Last updated: November 2025 · Reading time: 10–14 minutes · Audience: membrane/process engineers, EPCs, O&M teams
This practical guide contrasts RO antiscalants with cooling-water (circulating water) scale inhibitors—from chemistry and operating constraints to purity, dose windows, compatibility, acceptance criteria, and a field-tested selection framework.

Executive Summary — What’s the Real Difference?
- Mission & duty cycle: RO operates with short contact time, narrow flow channels, и high purity needs. Cooling-water programs run for months in open/recirculating loops with higher solids and bio-load tolerance.
- Chemistry: RO antiscalants emphasize fast threshold inhibition and low-impurity actives; cooling-water inhibitors rely more on polymeric dispersants and blends with corrosion inhibitors.
- Bottom line: Do not cross-use. Cooling-water products risk polymer fouling in RO; RO formulations lack the dispersancy and co-inhibitors needed for towers.
Focus phrase (for SEO): Many buyers search for “RO antiscalant vs cooling water antiscalant”—this guide provides a defensible answer with acceptance criteria and a decision tree.
Design Objectives & Operating Constraints
RO antiscalant — built for membranes
- Very short residence time → needs fast threshold inhibition and crystal modification.
- Avoids high-MW dispersants/cationic polymers that can plug spacers or bind membranes.
- High purity (low metals/insolubles) to minimize fouling; compatibility with polyamide limits (pH/temperature, oxidants).
Cooling-water antiscalant — built for recirculation
- Long duty cycles, high suspended solids tolerance, and frequent use of polymeric dispersants.
- Typically blended with corrosion inhibitors (e.g., zinc, molybdate, orthophosphate) and biocide programs.
- Large system volume → reagent purity requirements are looser than RO service.
RO Antiscalant vs Cooling-Water Antiscalant — Quick Comparison
| Attribute | RO Antiscalant | Cooling-Water Antiscalant | Operator Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary actives | Carboxylate/sulfonated copolymers; low-impurity phosphonates; silica inhibitors; iron control | Organophosphonates (ATMP, HEDP, DTPMP, PBTC), polyacrylates/MA copolymers, dispersants; often with corrosion inhibitors | RO limits cationics & high-MW polymers; towers welcome dispersants |
| Typical dose | 1–6 mg/L (projection-based) | 5–30 mg/L actives (COC/pH controlled) | RO uses projection software and normalized KPIs; towers use COC & coupons |
| Purity sensitivity | High — low insolubles/metals, biostable, membrane-safe | Moderate — blends acceptable; purity less critical | Cross-using tower chemicals in RO risks fouling |
| Best targets | CaCO₃, CaSO₄, Ba/SrSO₄, silica (within limits), Fe/Mn control | CaCO₃, Ca₃(PO₄)₂, iron scales, sludge dispersion; synergy with biocides | RO silica control needs tight windows; towers rely more on dispersancy |
| KPIs & acceptance | Stable normalized ΔP; stable salt rejection; SDI trend; product on spec | Target COC without scale; corrosion coupons (e.g., CS ≤ 3 mpy); clean inspection points | Define pass/fail criteria до optimization |
In practice, RO antiscalant vs cooling water antiscalant is a choice about duty cycle and purity: membranes need fast, clean threshold inhibition, while towers demand dispersancy and long-term robustness.
Application Windows & Dosing
RO systems
- Inject до cartridge filters; verify mixing energy and contact time.
- Set dose from projections (LSI, CaSO₄/BaSO₄/SrSO₄ limits, silica ceiling, recovery, temperature).
- Trend normalized ΔP, stage flows, salt rejection, permeate conductivity, SDI/NTU across prefilters.
Cooling towers / recirculating loops
- Control via cycles of concentration (blowdown), alkalinity/pH set-points, makeup water variability.
- Pair with a corrosion inhibitor and validated biocide plan; use coupons and deposit meters where available.
- Watch for phosphate/zinc interactions and precipitation limits at higher pH.
Purity, Fouling Risk & Compatibility
RO quality gates
- Low metals/insolubles; no cationic polyelectrolytes; avoid high-MW dispersants; biostable; compatible with membrane materials and CIP.
- Sequencing: coagulants/flocculants upstream must not interact; oxidants must respect polyamide limits.
Cooling-water formulations
- Multi-active blends acceptable; dispersant levels are often higher; performance proven with jar tests/coupon data.
- Compatibility with biocides/disinfectants and softening/acid feed is essential.
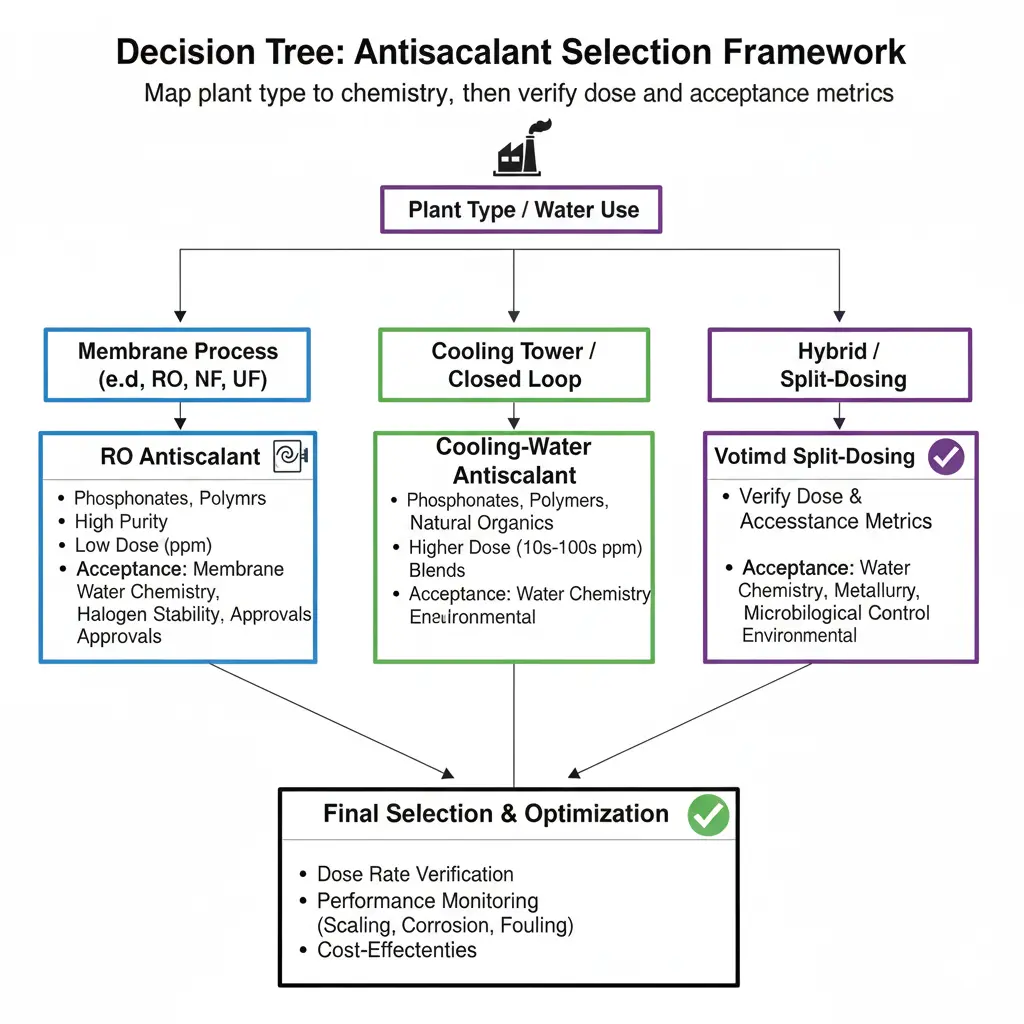
Selection Framework for RO Antiscalant vs Cooling Water Antiscalant
- Identify process: RO/NF/DTRO → choose an Антискалант для обратного осмоса.
- Project limits: sulfate scales, silica, recovery, temperature → set dose window and checks.
- Open recirculation (tower/loop): choose cooling-water antiscalant + corrosion inhibitor + biocide; control COC/pH.
- Hybrid plants: split-dosing; prevent back-flow of dispersant-rich tower water into RO pretreatment.
Cost, Compliance & ESG
- Dose-to-cost: convert mg/L to cost per 1,000 m³ of treated water or per MWh of cooling duty.
- Discharge compliance: phosphorus-limited permits may favor low-P or phosphorus-free options.
- Waste streams: RO concentrate vs. tower blowdown—confirm receiving limits for phosphate, metals and COD.
Acceptance Criteria & Troubleshooting
RO acceptance
- Normalized ΔP slope ≤ 4–5%/week; stable salt rejection; no SDI rise across prefilters; permeate quality on spec.
- When scaling persists: revisit projections, recovery, brine staging, pH strategy, and silica ceiling.
Cooling-water acceptance
- Target COC met with clean inspection points; corrosion coupons e.g., carbon steel ≤ 3 mpy (project-specific); deposit rate trend within limits.
- When deposits appear: verify pH/alkalinity control, makeup variability, biocide synergy, and solids removal (sidestream filtration).
References & Further Reading
- U.S. EPA — Water Research
- WHO — Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality
- USGS — Alkalinity & Water (buffers & scaling)
Need Help Choosing the Right Antiscalant?
Send your analysis (alkalinity, hardness, sulfate, silica, Fe/Mn, pH, temperature) and plant details. We’ll project scaling limits and size a dose with acceptance criteria you can audit.
If you’re comparing RO antiscalant vs cooling water antiscalant for a hybrid plant, split the programs and prevent tower chemistry from reaching RO pretreatment to avoid polymer fouling.
Water Treatment Solutions - Case Studies - Водные инструменты Stark - Блог - Запрос Цитировать
About the Author
Stark Water — process engineers focused on RO/UF/NF scaling control, cooling-water programs, and lifecycle-cost optimization.
FAQs — RO Antiscalant vs Cooling-Water Antiscalant
1) Can a cooling-water antiscalant be used in RO?
No. Dispersant-rich tower products and cationic components can foul membranes. Use a membrane-qualified RO antiscalant.
2) When do RO systems still scale despite antiscalant?
When projections are wrong, recovery is too high, pH/temperature change speciation, silica exceeds ceiling, or mixing/contact time is inadequate.
3) How do I choose between antiscalant and acid dosing in towers?
Balance alkalinity/pH set-points, COC and corrosion risk. Many plants use both: acid to control pH, antiscalant to manage precipitation and dispersion.
4) Are low-P/“green” products effective?
Yes in many cases, but confirm with jar tests/coupon data and ensure regulatory fit for blowdown phosphorus limits.
5) What tests confirm suitability?
For RO: projection + membrane cell tests and trend of normalized ΔP/rejection. For towers: jar tests, deposit tendency, and coupon corrosion rates.

