This engineer-to-engineer guide explains what a pure water system is, how RO/DI/EDI trains fit into modern plants, and how to size, specify, install and maintain systems with confidence. You’ll find decision maps, component questions, a quick sizing worksheet, a cost model, and an RFQ checklist.
Reviewed by Stark Water Process Engineering Team • Last updated: 20 Oct 2025
1) What a pure water system is & where it fits
A pure water system removes salts, hardness, organics and microbes to meet a defined product-water spec. Common trains:
- RO only (polishing elsewhere): general process water, beverage make-up, lab pre-treatment.
- RO → DI (mixed bed): high quality with regeneration chemicals; robust when CO2/silica are controlled.
- RO → EDI: continuous high resistivity without acid/caustic; needs good RO and interstage conditioning.
- RO → polishing (carbon/UF/UV/0.2 μm): low TOC and microbiological risk for bottling & point-of-use.
| Anmeldung | Typisches Ziel | Indicative train |
|---|---|---|
| Boiler make-up | 5–20 μS/cm | Pretreatment → RO → (optional) softener/MB |
| Food & beverage | 1–10 μS/cm; low TOC | Pretreatment → RO → carbon/UV → final filter |
| Lab/process | 0.055–1 μS/cm (18–1 MΩ·cm) | Pretreatment → RO → EDI or MB → polishing |
| Elektronik/UPW | 18 MΩ·cm; low silica/TOC | Pretreatment → RO → EDI → mixed-bed → UPW loop |
2) Pure Water System Quick decision map
- Target resistivity/conductivity: ≤1 μS/cm → add DI/EDI; ≥1 μS/cm → RO with polishing may be enough.
- Chemical policy: no acid/caustic on site → choose EDI; otherwise DI mixed bed is viable.
- CO2 & silica: if high, add interstage pH/degassing or choose DI mixed bed polishing.
- Micro/TOC risk: add carbon/UV/0.2 μm and hygienic loop design.
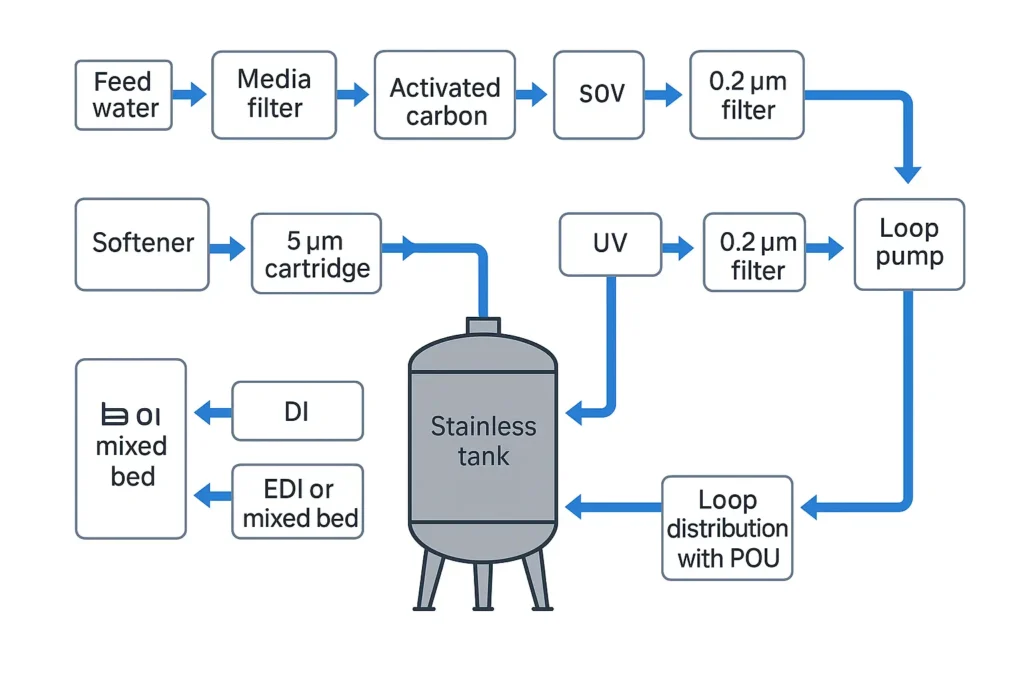
3) Source water drives design
Test TDS, hardness, alkalinity/CO2, iron/manganese, turbidity/SDI, chlorine/oxidants, and bacteria. Results decide pretreatment and RO recovery limits.
- Hardness → scale risk → softener/antiscalant + recovery limits.
- Iron/Mn → oxidize & filter before RO; pick non-fouling media.
- High SDI → multimedia or UF pretreatment.
- Free chlorine → activated carbon and/or SBS dosing to protect polyamide RO.
4) Key components & vendor questions
RO-Membranen
Ask for brand class, array (4040 vs 8040), design flux, recovery and validated replacement cycles. See 4040 vs 8040.
Hochdruckpumpe
Check duty point, efficiency, NPSH, seals and noise; match to temperature-corrected RO curve.
Vorbehandlung
MMF for solids, activated carbon for chlorine/organics, softener or antiscalant for hardness, UF when SDI is unstable.
Instrumentation & controls
Pressures & ΔP, flows, temperature, feed/permeate conductivity, ORP, pH (interstage), tank levels, event logging.
Skid hygiene
CIP ports, drainable low points, labeled piping and safe chemical access.
5) Sizing essentials
| Schritt | Faustformel | Anmerkungen |
|---|---|---|
| Average flow | From process demand (m³/h) | Prefer measured data |
| Erholung | 60–85% typical | Respect scale/fouling limits |
| Peak factor | 1.3–1.6× | Size tank + loop to cover peaks |
| Loop velocity | 0.9–1.5 m/s | Micro control via turbulence |
| Final filter | 0.2–0.45 μm integrity-testable | Beverage & sensitive tools |
6) Materials & workmanship
- SS316 for sanitary/high-temp loops; SS304 for frames/common headers.
- uPVC/PPR acceptable on cold non-sanitary runs within rating.
- Compatible elastomers (EPDM/FKM/PTFE), clean welds, drainability.
See stainless-steel tanks & housings.
7) Installation, training & warranty
- Commissioning with instrument calibration and baseline logs.
- Operator training—start/stop, CIP/SIP, chemical safety, daily checks.
- 12-month warranty from start-up; optional extensions.
- Spares: cartridges, O-rings, SBS/antiscalant, pump seal kit, membrane end-caps.
8) Cost of ownership
Model electricity (pump kWh), chemicals (SBS/antiscalant/cleaners), membranes & cartridges, labor and sanitation cadence. Quick checks: RO OPEX-Rechner.
9) Compliance & documentation
- P&IDs, wiring diagrams, instrument ranges & alarm setpoints.
- FAT/SAT with acceptance data and baseline logs.
- PM schedule and validated CIP/SIP procedures.
- Align claims to WQA resources und ASTM D1193 when applicable.
10) RFQ template (copy & paste)
| Company & site | - |
|---|---|
| Average / peak demand | — m³/h / — m³/h |
| Target quality | — μS/cm (or — MΩ·cm); silica ≤ — mg/L; TOC ≤ — ppb |
| Speisewasser | TDS —; hardness — as CaCO₃; SDI —; Fe/Mn —/—; free Cl₂ —; pH — |
| Preferred train | RO / RO+DI / RO+EDI / RO+polish |
| Materials | SS316 / SS304 / uPVC / PPR; tank & loop spec |
| Utilities | Power —, compressed air —, drain — |
| Kontrolliert | PLC/HMI brand, remote I/O, data logging |
| Delivery & services | Delivery date, installation/commissioning, training, warranty |
11) FAQs
RO vs DI vs EDI—what’s best for my plant?
RO for bulk desalting; DI for highest resistivity with chemical regeneration; EDI for continuous high resistivity without acid/caustic when interstage CO₂/silica are controlled.
How long do RO membranes last?
Typically 3–5 years with stable pretreatment and periodic CIP; see our membrane care guide.
Stainless vs plastic piping?
SS316 for sanitary/high-temp loops; SS304 for frames/headers; uPVC/PPR for cold non-sanitary runs as allowed.
Internal links: RO membrane housing diagram - Stainless-steel tanks & housings - LSI-Rechner - Chlorine dosage calculator
Technical guidance only—verify with your feed tests and OEM instructions.

