Summary. This hands-on guide explains the top reasons RO membrane life becomes short in industrial systems and how to extend it with better startup/shutdown, pretreatment, chemistry control, and preventive maintenance. Use the checklists, tables, and decision trees below to reduce downtime and protect your modules.
By Stark Water Process Engineering Team | Last reviewed: 28 Oct 2025
Executive snapshot — top causes that shorten RO membrane life
- Air entrainment & water hammer during start/stop.
- Improper shutdown & flushing (concentrate left saturated → scaling/biofouling).
- Biofouling from weak disinfection/preservation or long idle periods.
- Scaling & colloids (CaCO₃/CaSO₄/Ba/Sr/SiO₂; iron/aluminum; organics).
- Oxidant/chemical attack (free Cl₂, incompatible solvents, extreme pH/T).
- Over-flux & pressure cycling causing mechanical stress.
- Pretreatment failures (high SDI/turbidity, poor carbon/UF/filtration upkeep).
- Seal/O-ring/bypass issues and incorrect assembly.
- Cleaning mistakes (wrong chemistry/sequence; inadequate rinse).
- Storage & preservation errors (concentration, contact time, changeout).
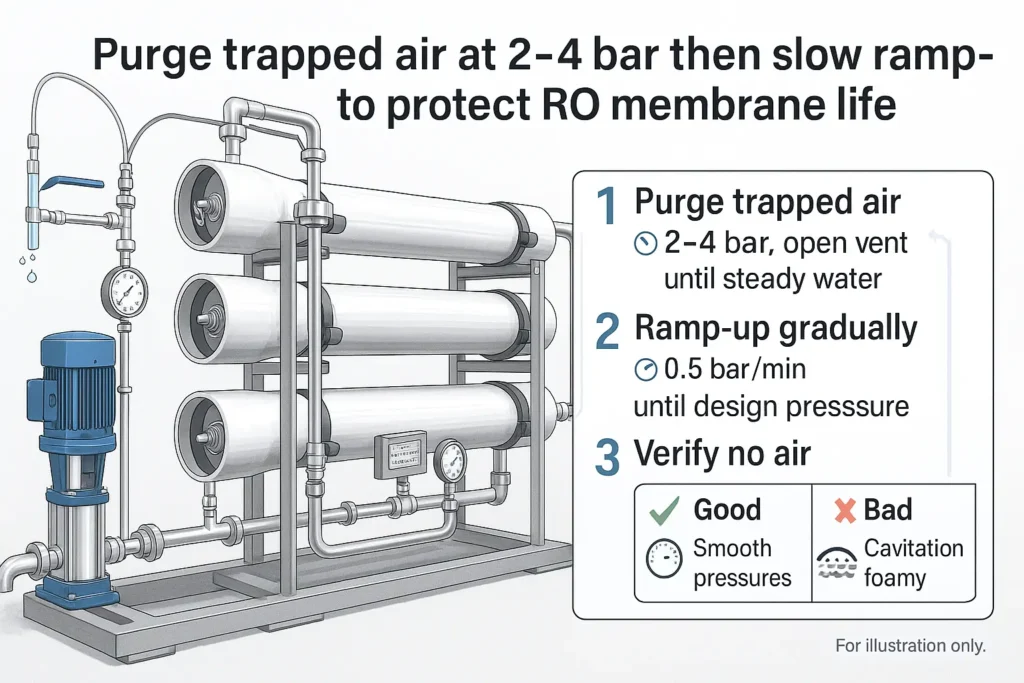
1) Air entrainment & water hammer
Symptoms: sudden salt passage spikes after restart, noisy cavitation, fluctuating ΔP, spacer/leaf mechanical damage.
Root causes: trapped air after maintenance or shutdown; negative pressure suction at fittings; fast valve moves.
How to protect RO membrane life: purge air at low pressure (2–4 bar) until flowmeters show no bubbles, then ramp pressure slowly; fix suction leaks; replace clogged prefilters; avoid instant valve changes.
2) Improper shutdown & flushing
Never stop with chemical feed on or with saturated concentrate inside elements. The right sequence:
- Stop chemical dosing; hold for a short mixing time.
- Reduce to ~3 bar and flush with pretreated water for ~10 min until brine TDS ≈ feed.
- Depressurize gradually; isolate and drain low points if freezing risk exists.
Good shutdown discipline alone measurably extends RO membrane life.
3) Biofouling from weak disinfection/preservation
Why it hurts RO membrane life: biofilm raises ΔP, blocks feed channels, and accelerates chemical consumption.
Controles: sanitize skids before commissioning; schedule routine online disinfection; apply manufacturer-approved preservation for idle periods and refresh on cadence; verify compatibility with polyamide.
4) Scaling & colloidal fouling
Manage recovery, antiscalant dose, and pH/CO₂ to stay inside saturation limits. Use front-end softening/iron-manganese removal/UF where needed. Target SDI ≤ 3–5. Diagnose silica separately (pH, coagulants, magnesia or polishing steps).
LSI-rekenmachine - Permeate blending calculator
5) Oxidant & chemical attack
- Free chlorine/monochloramine: keep 0 mg/L at membranes; use online ORP/Cl₂ monitoring and reducing agent control.
- CIP chemistry: follow vendor compatibility; avoid extreme pH/temperature and solvent exposure.
6) Over-flux, pressure cycling & hydrodynamics
Respect design flux and interstage hydraulics. Avoid rapid starts/stops and hard valve slams. Consider stage recycle or backpressure control to stabilize crossflow and protect RO membrane life.
7) Pretreatment: small misses, big impact
- Track raw-water variability and SDI/turbidity continuously.
- Maintain MMF/UF filters, carbon beds, and 5 μm cartridges.
- Log ORP/free-chlorine; ensure complete dechlorination upstream.
8) Seals, O-rings & bypass
Mis-seated end caps, dry O-rings, and missing spacers cause internal bypass and localized over-flux. Lubricate O-rings with compatible lubricant, torque per spec, and pressure-test after service.
9) Cleaning mistakes & preservation errors
Goede praktijken: low-pressure/low-flow circulation → soak → high-flow rinse; use separate acids/alkalis for scale/organics; fully neutralize and rinse before return to service. For idle >24–48 h, switch to approved preservation and label tanks/lines.
RO commissioning guide - Chloordosering calculator
10) Operating limits (quick reference)
| Parameter | Typical limit / note |
|---|---|
| Free Cl₂ at membrane | 0 mg/L (use ORP/Cl₂ monitoring + SBS control) |
| SDI | ≤ 3–5 (site-specific) |
| pH (continuous / cleaning) | 2–11 / 1–12 (follow element data sheet) |
| Temperatuur | ≤ 45 °C (or vendor spec) |
| ΔP per stage | Follow design; investigate rapid rise |
11) Diagnostics — normalize & decide fast
Trend these KPIs to protect RO membrane life and triage root cause:
- NPF (normalized permeate flow), salt passageen ΔP by stage.
- ATP/bioburden, particle counts, Fe/Mn & silica, SDI/turbidity, residual Cl₂/ORP.
| Observed change | Likely cause | First actions |
|---|---|---|
| ΔP ↑, NPF ↓, salt passage stable | Fouling (scale/colloid/bio) | Check SDI/antiscalant; choose acid/alkaline CIP; verify shutdown flush |
| Salt passage ↑ after restart | Trapped air / pressure shock | Purge at 2–4 bar; slow ramp; inspect for suction leaks |
| Salt passage ↑ with ORP/Cl₂ drift | Oxidant attack risk | Correct dechlorination/SBS; verify sensors; review carbon health |
12) Preventive maintenance schedule
- Daily: log ΔP, NPF, salt passage, ORP/Cl₂, SDI; visual leak check.
- Weekly: cartridge change as needed; verify pump seals and valves; hygiene checks.
- Monthly: online disinfection; audit shutdown/flush quality; calibrate sensors.
- Quarterly / as-needed: CIP per diagnostics; refresh preservation solutions.
FAQs
Why does salt passage spike after a good restart?
Residual air or a fast pressure ramp can cause channel maldistribution. Always purge at low pressure until bubble-free, then ramp slowly to design pressure.
How do I extend RO membrane life on high-silica feeds?
Control recovery, pH/temperature, and use silica-focused antiscalants or polishing (e.g., weak-base anion or EDI feed conditioning). Manage shutdown flushes diligently.
Is short exposure to chlorine acceptable?
No free chlorine at the membrane. Maintain zero at the element inlet, proven by ORP/Cl₂ monitoring and periodic wet-chemistry checks.
Volgende stappen (RFQ & interne links)
Share your feed analysis and demand curve—our team will size antiscalant, interstage hydraulics, preservation strategy and a hygienic CIP package to maximize RO membrane life.
RO commissioning - RO shutdown & preservation - Chloordosering calculator - LSI calculator - RO OPEX calculator

