This engineer-to-engineer guide explains what a pure water system is, how RO/DI/EDI trains fit into modern plants, and how to size, specify, install and maintain systems with confidence. You’ll find decision maps, component questions, a quick sizing worksheet, a cost model, and an RFQ checklist.
Reviewed by Stark Water Process Engineering Team • Last updated: 20 Oct 2025
1) What a pure water system is & where it fits
A pure water system removes salts, hardness, organics and microbes to meet a defined product-water spec. Common trains:
- RO only (polishing elsewhere): general process water, beverage make-up, lab pre-treatment.
- RO → DI (mixed bed): high quality with regeneration chemicals; robust when CO2/silica are controlled.
- RO → EDI: continuous high resistivity without acid/caustic; needs good RO and interstage conditioning.
- RO → polishing (carbon/UF/UV/0.2 μm): low TOC and microbiological risk for bottling & point-of-use.
| Zastosowanie | Typowy cel | Indicative train |
|---|---|---|
| Boiler make-up | 5–20 μS/cm | Pretreatment → RO → (optional) softener/MB |
| Food & beverage | 1–10 μS/cm; low TOC | Pretreatment → RO → carbon/UV → final filter |
| Lab/process | 0.055–1 μS/cm (18–1 MΩ·cm) | Pretreatment → RO → EDI or MB → polishing |
| Elektronika/UPW | 18 MΩ·cm; low silica/TOC | Pretreatment → RO → EDI → mixed-bed → UPW loop |
2) Pure Water System Quick decision map
- Target resistivity/conductivity: ≤1 μS/cm → add DI/EDI; ≥1 μS/cm → RO with polishing may be enough.
- Chemical policy: no acid/caustic on site → choose EDI; otherwise DI mixed bed is viable.
- CO2 & silica: if high, add interstage pH/degassing or choose DI mixed bed polishing.
- Micro/TOC risk: add carbon/UV/0.2 μm and hygienic loop design.
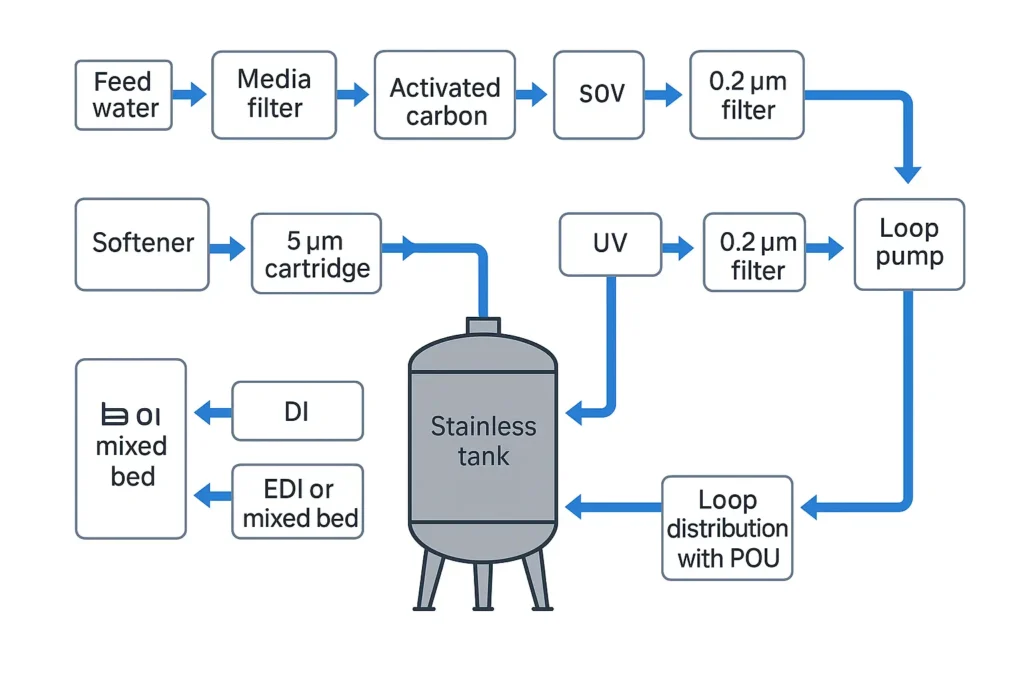
3) Source water drives design
Test TDS, hardness, alkalinity/CO2, iron/manganese, turbidity/SDI, chlorine/oxidants, and bacteria. Results decide pretreatment and RO recovery limits.
- Hardness → scale risk → softener/antiscalant + recovery limits.
- Iron/Mn → oxidize & filter before RO; pick non-fouling media.
- High SDI → multimedia or UF pretreatment.
- Free chlorine → activated carbon and/or SBS dosing to protect polyamide RO.
4) Key components & vendor questions
Membrany RO
Ask for brand class, array (4040 vs 8040), design flux, recovery and validated replacement cycles. See 4040 vs 8040.
Pompa wysokociśnieniowa
Check duty point, efficiency, NPSH, seals and noise; match to temperature-corrected RO curve.
Obróbka wstępna
MMF for solids, activated carbon for chlorine/organics, softener or antiscalant for hardness, UF when SDI is unstable.
Instrumentation & controls
Pressures & ΔP, flows, temperature, feed/permeate conductivity, ORP, pH (interstage), tank levels, event logging.
Skid hygiene
CIP ports, drainable low points, labeled piping and safe chemical access.
5) Sizing essentials
| Krok | Rule of thumb | Uwagi |
|---|---|---|
| Average flow | From process demand (m³/h) | Prefer measured data |
| Odzyskiwanie | 60–85% typical | Respect scale/fouling limits |
| Peak factor | 1.3–1.6× | Size tank + loop to cover peaks |
| Loop velocity | 0.9–1.5 m/s | Micro control via turbulence |
| Final filter | 0.2–0.45 μm integrity-testable | Beverage & sensitive tools |
6) Materials & workmanship
- SS316 for sanitary/high-temp loops; SS304 for frames/common headers.
- uPVC/PPR acceptable on cold non-sanitary runs within rating.
- Compatible elastomers (EPDM/FKM/PTFE), clean welds, drainability.
See stainless-steel tanks & housings.
7) Installation, training & warranty
- Commissioning with instrument calibration and baseline logs.
- Operator training—start/stop, CIP/SIP, chemical safety, daily checks.
- 12-month warranty from start-up; optional extensions.
- Spares: cartridges, O-rings, SBS/antiscalant, pump seal kit, membrane end-caps.
8) Cost of ownership
Model electricity (pump kWh), chemicals (SBS/antiscalant/cleaners), membranes & cartridges, labor and sanitation cadence. Quick checks: Kalkulator RO OPEX.
9) Compliance & documentation
- P&IDs, wiring diagrams, instrument ranges & alarm setpoints.
- FAT/SAT with acceptance data and baseline logs.
- PM schedule and validated CIP/SIP procedures.
- Align claims to WQA resources oraz ASTM D1193 when applicable.
10) RFQ template (copy & paste)
| Company & site | - |
|---|---|
| Average / peak demand | — m³/h / — m³/h |
| Target quality | — μS/cm (or — MΩ·cm); silica ≤ — mg/L; TOC ≤ — ppb |
| Feed water | TDS —; hardness — as CaCO₃; SDI —; Fe/Mn —/—; free Cl₂ —; pH — |
| Preferred train | RO / RO+DI / RO+EDI / RO+polish |
| Materiały | SS316 / SS304 / uPVC / PPR; tank & loop spec |
| Utilities | Power —, compressed air —, drain — |
| Controls | PLC/HMI brand, remote I/O, data logging |
| Delivery & services | Delivery date, installation/commissioning, training, warranty |
Zapytanie ofertowe More Guides
11) FAQs
RO vs DI vs EDI—what’s best for my plant?
RO for bulk desalting; DI for highest resistivity with chemical regeneration; EDI for continuous high resistivity without acid/caustic when interstage CO₂/silica are controlled.
How long do RO membranes last?
Typically 3–5 years with stable pretreatment and periodic CIP; see our membrane care guide.
Stainless vs plastic piping?
SS316 for sanitary/high-temp loops; SS304 for frames/headers; uPVC/PPR for cold non-sanitary runs as allowed.
Internal links: Schemat obudowy membrany RO - Stainless-steel tanks & housings - LSI calculator - Kalkulator dawki chloru
Technical guidance only—verify with your feed tests and OEM instructions.

