Water filtration iron removal parts are the service kits, media, valves, tanks and internals that keep iron and manganese filters running reliably. This guide gives you a pro overview of the process train, a parts catalog you can act on, quick sizing & backwash tables, BOM templates, troubleshooting, FAQs, and RFQ links. Use it to scope projects faster and reduce downtime.
1) Where Water Filtration Iron Removal Parts Fit in the Process
Typical industrial train:
- Oxidation — air injection (AIO) or chlorination/ozone.
- Contact & mixing — stainless-steel contact tank or static mixer.
- Catalytic filtration — MnO₂/Katalox Light/Greensand Plus to capture oxidized iron/manganese and suppress H2S.
- Polishing — carbon to remove residual oxidants/odors.
Illustration suggestion (Alt): “Iron removal process train and required parts — AIO/chlorination → contact tank → catalytic filter → carbon.”

2) Core Iron Removal Filter Parts Catalog — Quick Reference
| Category | Typical items | Key specs & notes | Common replacements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control valves | Fleck 2510/2750/2850/5810/5812/9500; Clack WS1/1.25/1.5/2.0 | Port size, service/backwash flow, drain size, power, programming (AIO/Filter) | Seal & spacer kits, piston kits, injector sets, brine/air check |
| Pressure vessels | FRP 10×54–24×72; 304/316L stainless housings | Diameter×height, pressure rating, port, internal riser ID, distributor interface | Manway gasket, sight-glass/O-rings, gauge set |
| Media | Katalox Light, Greensand Plus, MnO₂ (natural/coated), Birm, catalytic carbon, inert gravel | Service rate, BW rate (temp-corrected), pH/ORP window, oxidant demand | Top-up or full rebed per ΔP/bleed-through/pressure loss |
| AIO & mixing | Air intake/vent valves, injectors, static mixer, contact tank | Air draw & vent capacity, CT (contact time) target, gas management | Vent seals, injectors, vacuum breaker |
| Internals | Riser/center tube, upper/lower distributors, laterals, strainers | Distribution area, slot size, riser OD/ID & length, snap-ring type | Distributor baskets/screens, O-rings, riser couplers |
| Dosing | NaOCl/KMnO₄ pumps, solution tanks, rotameters, injection quills | Turn-down ratio, chemical compatibility, interlocks with flow | Diaphragms, tubing, foot valves, check valves |
| Instrumentation | ΔP gauges, flow meters, ORP/free Cl, sample valves, check valves | Scale range, wetted materials (NSF/ANSI), temperature limits | Gauge seals, sensor caps, probe O-rings |
Explosion diagram suggestion (Alt): “Iron filter internal parts — center tube, upper/lower distributors, media layering (inert–catalytic–carbon).”
3) Quick selection cards
- Low iron (≤3 mg/L, no odor): AIO + catalytic media (e.g., Katalox Light); verify backwash capacity.
- 3–5 mg/L iron or H2S/iron bacteria present: Chlorination + contact tank → catalytic filter → carbon polish.
- Iron & manganese both elevated: MnO₂ or Greensand+; design higher backwash & ORP control.
See related components: stainless-steel contact tanks & housings • chlorine dosage calculator
4) Iron Filter Sizing & Backwash Guide
4.1 Service & backwash rates (reference)
| Media | Service rate (gpm/ft²) | Backwash rate (gpm/ft² @ 20 °C) | Uwagi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Katalox Light | 5–12 | 10–16 | Temp-correct: +15–20% @ 10 °C. Good Fe/Mn/H2S. |
| Greensand Plus | 5–10 | 12–15 | Needs oxidant (NaOCl/KMnO₄) & ORP control. |
| MnO₂ (dense) | 5–10 | 15–25 | High BW demand; check drain hydraulics. |
| Catalytic carbon | 3–6 | 10–12 | Used in polish; chlorine reduction & odor. |
Backwash temperature correction: lower water temperature increases required BW rate; confirm with media datasheet.
4.2 Contact time (CT)
When chemical oxidation is used, size contact tank for the target CT (e.g., free Cl: 0.5–2.0 min depending on spec). Add static mixer to improve mass transfer.
4.3 Valve & drain sizing
- Match valve port and drain size to peak BW rate.
- Verify site drain capacity & backwash pump curve.
- Set interlocks for low/high level and chemical feed.
Chart suggestion (Alt): “Backwash rate chart for Katalox Light, MnO₂ and Greensand Plus with temperature correction.”
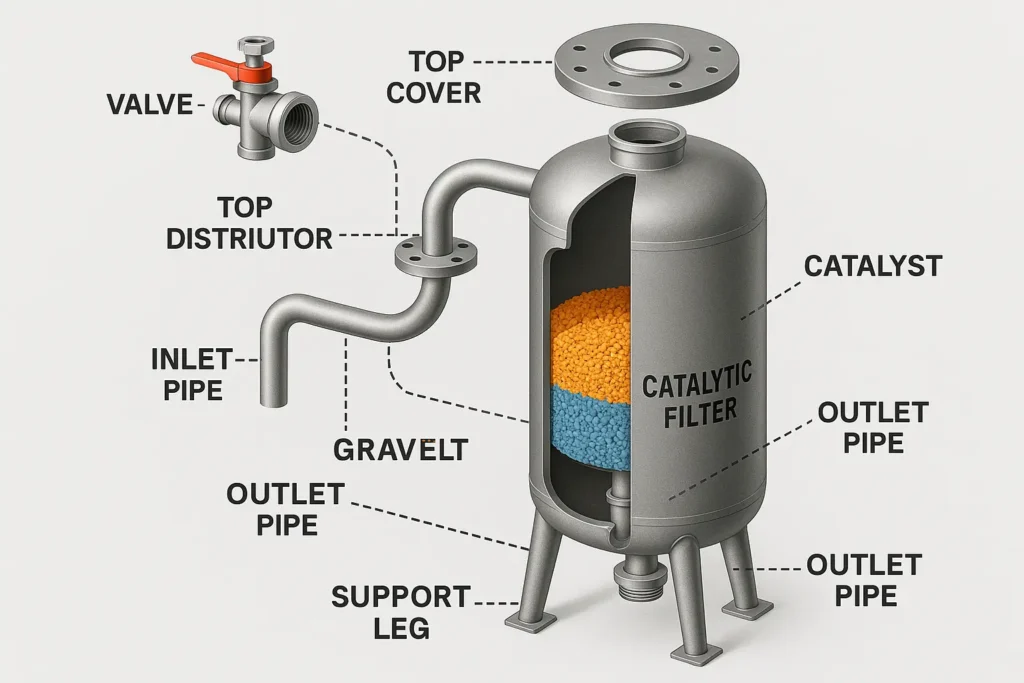
5) BOM templates (copy & adapt)
5.1 18×65 FRP iron filter (AIO)
- Valve: Fleck 5810 AIO (1.25″), drain 1″, power 120/240 V
- Tank: 18×65 FRP, 2.5″ NPSM
- Internals: 1.05″ riser, upper/lower baskets, inert gravel 1–3 mm/3–5 mm
- Media: Katalox Light xx kg (per datasheet), top-up 5–10%
- Vent/air release & vacuum breaker
- Instrumentation: ΔP gauges, sample valves
- Spare kits: seals & spacers, piston kit, injector set, O-rings
5.2 24×72 SS filter (chlorination + contact tank)
- Feed: NaOCl dosing pump + static mixer
- Contact tank: 316L, CT ≥ spec (with vent & drain)
- Valve: Fleck 2850/9500 (2″), or automated SS valves + PLC
- Media: MnO₂/Greensand Plus per calculation
- Polish: activated carbon 24×72
- Instrumentation: ORP/free Cl, flow meters
6) Iron Removal Filter Troubleshooting & Replacement Guide
| Symptom | Likely root causes | Fast checks / actions | Replace? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron bleed-through | Service rate too high; exhausted media; low ORP; channeling; iron bacteria | Drop service rate; verify ORP; shock chlorination; relevel bed; check injectors | Rebed media if performance not recovered |
| ΔP keeps rising | Fouling by fines/iron sludge; under-rated backwash; cold water | Increase BW rate/time; raise water temperature if possible; flush side strainers | Replace baskets/strain ers if damaged |
| H2S odor after filter | Insufficient oxidation/CT; venting issues | Increase oxidant dose; lengthen CT; fix air vent | Polish with catalytic carbon if needed |
| Valve won’t draw air/chem | Injector clogged; checks failed; seal wear | Clean/replace injector; rebuild checks; install kit | Seal & spacer kit / piston kit |
Typical cycles: media 2–5 years (water dependent), seal/spacer 1–2 years, injector/vent annually, gauges/probe O-rings as inspected.
7) Compliance & materials
- Use wetted materials compliant with applicable NSF/ANSI standards for drinking water where required.
- Check media/vendor datasheets for service & backwash envelopes and safety notes.
- Document ORP/free chlorine, flow, ΔP, and backwash events in your O&M log.
External references: WQA • ASTM
8) FAQs
Is AIO enough or should I chlorinate?
AIO works well at modest iron without heavy odor or biofouling. When H2S, iron bacteria or higher iron are present, chlorination + contact tank → catalytic filter → carbon polish is more robust.
Katalox Light vs Greensand Plus?
Both remove Fe/Mn. KL typically needs less chemical support and handles H2S well; Greensand Plus typically runs with NaOCl/KMnO₄ support and clear ORP control. Size by datasheet envelopes.
Why is my backwash weak?
Check temperature correction, drain/valve sizing, BW time, and supply pressure. Cold water can require 15–25% higher BW rate.
How often should I replace parts?
Plan annual kits for seals/spacers, injectors, vent checks; rebed media when ΔP, iron bleed or capacity trends indicate exhaustion.
9) Next steps (RFQ & internal links)
- Zapytanie ofertowe — share water analysis, flow profile and site utilities; we’ll size valves, media and tanks and send a parts list.
- Stainless-steel contact tanks & housings
- Chlorine dosage calculator
- RO membrane housing diagram (for upstream conditioning context)
Author: Stark Water Engineering Team — industrial filtration & process water projects since 2010. Last reviewed: 2025-10-20.

