ro membrane vs ro filter is a core distinction in any RO system. The membrane performs desalination by rejecting dissolved salts, while filters around it handle particles, chlorine/chloramine, and taste. Understanding this difference prevents early failure, saves operating cost, and keeps water quality stable.
Shop RO Membranes Shop RO Filters (PP/CTO/T33)
Quick Answer
Membrane = desalination; Filters = protection & polishing. If TDS is high or taste is salty, check the membrane. If flow is low or the membrane clogs early, check prefilters (PP/CTO). If taste/odor persists at normal TDS, check the post-carbon filter.
RO Membrane vs RO Filter (Definition & Diagram)
An Membrana RO is a thin-film composite element that removes ions via selective diffusion; an RO filter refers to the pre/post cartridges such as PP sediment, carbon block (CTO), and post-carbon. In short: membrane = desalination, filters = protection & polishing. When people search for ro membrane vs ro filter, they usually want to know which part to change first to fix taste, TDS, or flow.
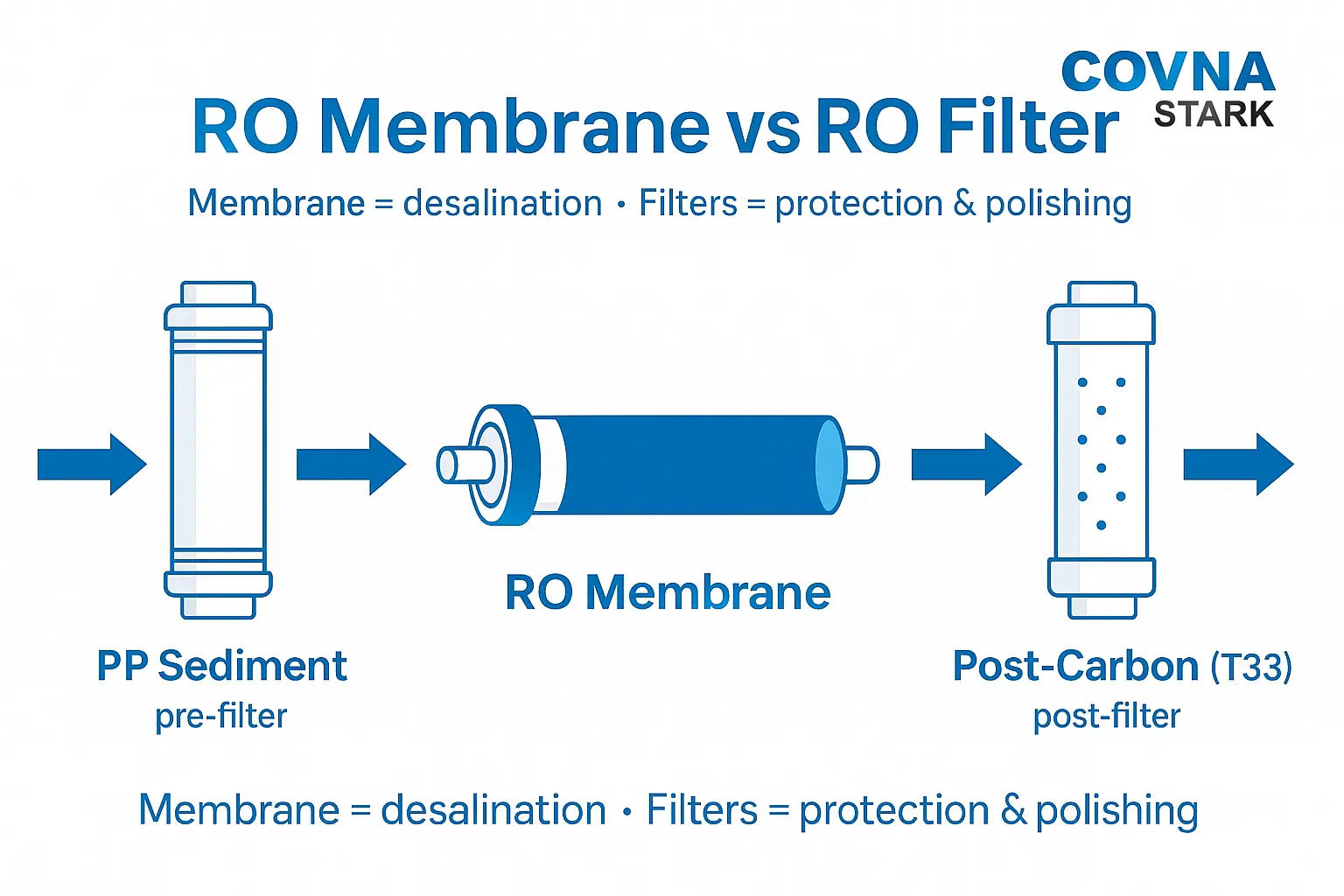
What Is an RO Membrane?
The RO membrane is a spiral-wound, semi-permeable barrier that rejects dissolved ions and small organics. Typical sizes and uses:
- 1812/2012 – under-sink household systems
- 4040 – commercial/light industrial skids
- 8040 – industrial BWRO/SWRO trains
See our Substituição da membrana RO guide for step-by-step change procedures.
Replacement Timing & Cost
Think in layers. Cartridges are cheap “sacrificial” parts, while the membrane is the high-value core. Use these practical triggers:
- PP sediment: replace when pressure drop rises or visibly dirty; typical 1–3 months for POU, weeks–months for industrial skids.
- CTO carbon block: replace by chlorine capacity or when free chlorine is detected upstream of RO; immediate action protects the membrane.
- Post-carbon: replace for taste/odor complaints at normal TDS.
- Membrana RO: replace when permeate TDS increases and normalized flow falls 15–25% and cannot be restored by cleaning.
Budget tip: keeping cartridges fresh typically extends membrane life from months to years. If you are comparing ro membrane vs ro filter from a cost angle, always protect the expensive part (membrane) by changing the inexpensive filters on time.
Reference: AMTA – Cleaning in Place (CIP) factsheet | NSF/ANSI 58 overview
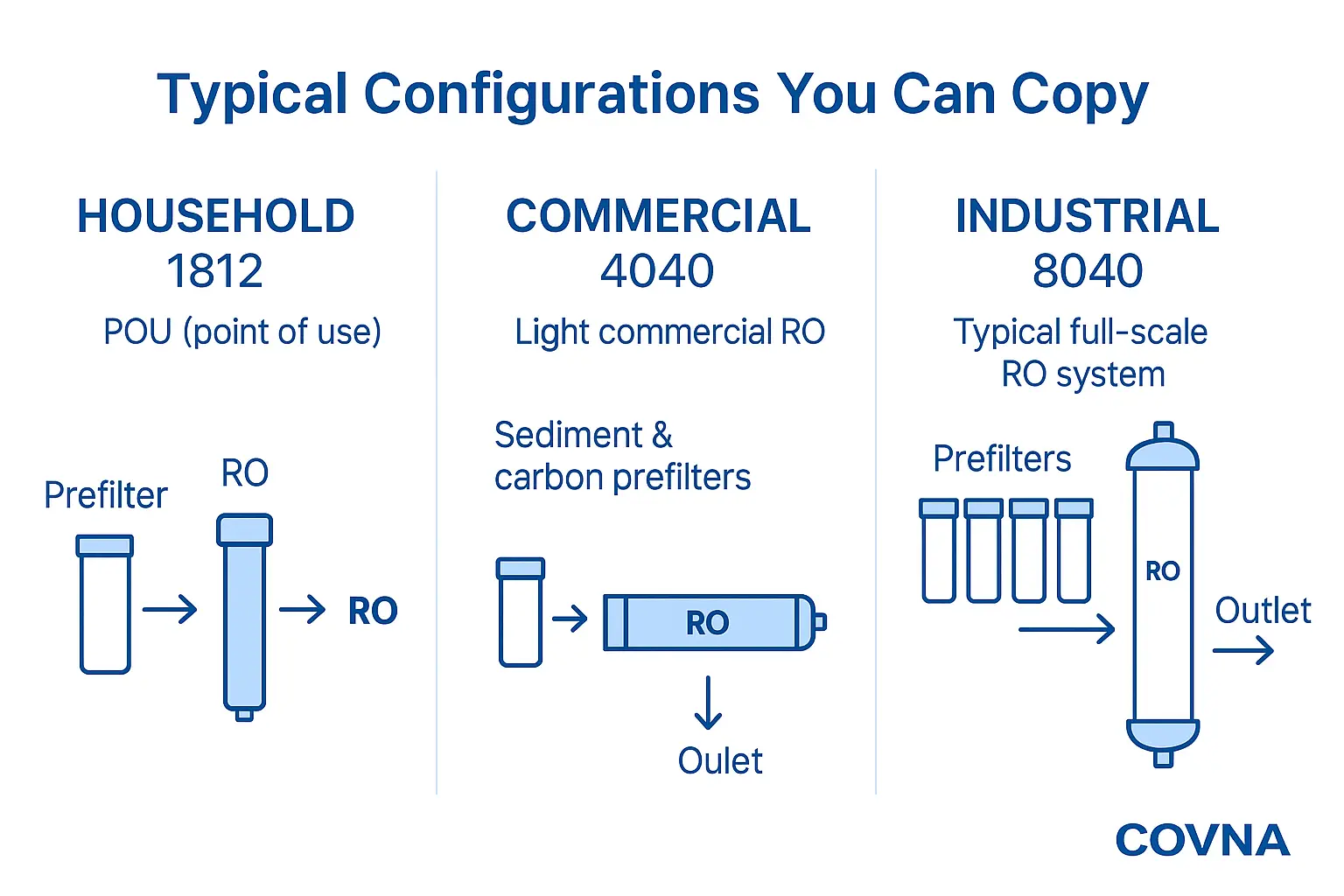
Typical Configurations You Can Copy
Household 1812 POU
PP 5 µm → CTO carbon block → Membrana RO (1812) → post-carbon (T33). If TDS stays high, swap the membrane; if flow is weak, swap the PP; if chlorine breakthrough occurs, change CTO first.
Commercial 4040 Coffee Shop / Lab
20 µm cartridge → softener or antiscalant → 5 µm cartridge → CTO → Membrana RO (4040) → blend valve or DI polish. Use SDI ≤ 3 and monitor ΔP across the vessel.
Industrial 8040 BWRO/SWRO
Media filtration/UF → dechlorination → 5 µm cartridges → antiscalant → high-pressure pump → Membrana RO (8040 trains). Plan periodic CIP and proper preservation during shutdowns.
Need sizing? Try the Calculadora de dimensionamento de RO or see our Substituição da membrana RO checklist.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Running without a carbon block on chlorinated feed → oxidation destroys TFC membranes.
- Overshooting recovery → scaling and rapid fouling; keep SDI in control.
- Confusing ro membrane vs ro filter during troubleshooting → replace filters first for flow/pressure issues, the membrane for TDS/rejection issues.
- Skipping preservation during long shutdowns → biofouling and irreversible damage.
What Are RO Filters?
RO systems use several filters around the membrane:
- PP Sediment (e.g., 5 μm) – captures rust/sand; protects pumps and the membrane.
- CTO Carbon Block – removes chlorine/chloramine and organics to prevent membrane oxidation and fouling.
- Post-Carbon (T33/Polishing) – adsorbs residual taste/odor after RO.
- Optional: softener/antiscalant for hardness control; UV for microbial risk.
RO Membrane vs RO Filter – Side-by-Side Comparison
| Item | Function | Pore / MWCO | Material (typ.) | Typical Lifespan | Where It Sits | Cost (rel.) | Failure Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RO Membrane | Removes dissolved salts (desalination) | < 1 nm (selective diffusion) | Thin-film composite (TFC) | 18–36 mo (1812); 12–24 mo (4040); 2–5 yrs (8040) | Between prefilters and post-polish | High | Permeate TDS↑, flow↓; salty taste; ΔP↑ not recoverable by cleaning |
| PP Sediment Filter | Removes particulates/colloids | 1–20 μm (commonly 5 μm) | Polypropylene melt-blown | 1–3 months (household); weeks–months (industrial) | Upstream of membrane | Low | Flow↓, pressure drop↑; visible dirt |
| CTO Carbon Block | Dechlorination & organics adsorption | Adsorptive (effective < 1 μm nominal) | Activated carbon block | 3–6 months or by chlorine capacity | Upstream of membrane | Low–Medium | Chlorine breakthrough → membrane damage risk; taste/odor returns |
| Post-Carbon (T33) | Polishing taste/odor after RO | Adsorptive | Granular/pressed carbon | 6–12 months | Downstream of membrane | Low | Taste/odor complaints at normal TDS |
Do I Need Both a Membrane and Filters?
Yes. Prefilters protect the membrane and extend its life; the membrana provides desalination; the post-filter polishes taste. Removing any stage shortens membrane life or compromises water quality.
See our in-depth guide on ro membrane replacement for the step-by-step procedure.
Browse ro membrane vs ro filter kits to match cartridges and membranes for your system.
Which Should I Replace First?
- High TDS or salty taste → Diagnose membrane first; confirm with TDS/rejection test.
- Low flow / ΔP↑ → Replace PP sediment; check CTO for plugging.
- Chlorine detected upstream of RO → Replace CTO immediately to protect the membrane.
- Taste/odor at normal TDS → Replace post-carbon.
When the membrane no longer recovers after cleaning, perform a full Substituição da membrana RO.
Buying Guide & Model Matching
- Confirm size – 1812/2012 (household), 4040 (commercial), 8040 (industrial).
- Check housing & interconnectors – match permeate tube diameter and brine-seal direction.
- Match recovery & pressure ratings – ensure system design won’t exceed limits.
- Pick the correct filter micron & carbon capacity for your feed water (SDI, chlorine).
Select RO Membranes Select RO Filters Use RO Sizing Calculator
FAQs
Is a membrane the same as a filter?Can I run an RO without a carbon block?How often should I change filters vs the membrane?Does a post-carbon filter reduce TDS?Which part improves flow?
Need Help Choosing?
Send us your feed TDS, SDI, target flow, and operating pressure. We’ll recommend the right membrane plus PP/CTO set and provide pricing.
