Reverse osmosis (RO) systems are widely used in industrial, commercial, and municipal water treatment applications. However, many operators face challenges such as membrane fouling, unstable performance, and frequent membrane replacement. In practice, the durability of a reverse osmosis system does not depend on a single component, but on a combination of pretreatment design, operating conditions, chemical control, and proper system management.
This article provides practical, engineering-based guidance on how to improve reverse osmosis system durability, extend membrane lifespan, and ensure stable long-term operation.
Key Factors That Affect Reverse Osmosis System Durability
The long-term reliability of an RO system is influenced by several interrelated factors, including:
- Feed water quality and seasonal variations
- Pretreatment system design and performance
- Chemical selection and dosing control
- Operating parameters such as pressure, recovery rate, and temperature
- Operator experience and maintenance management
Ignoring any one of these factors may significantly shorten membrane life and increase operating costs.
The Critical Role of Pretreatment Systems in Extending RO System Lifespan
Pretreatment Design Considerations for Different Water Sources
Pretreatment is one of the most important factors affecting reverse osmosis system durability. For groundwater sources, conventional pretreatment such as quartz sand filtration and activated carbon filtration is often sufficient. However, surface water typically contains higher levels of suspended solids, organic matter, and biological contaminants, requiring more careful pretreatment design.
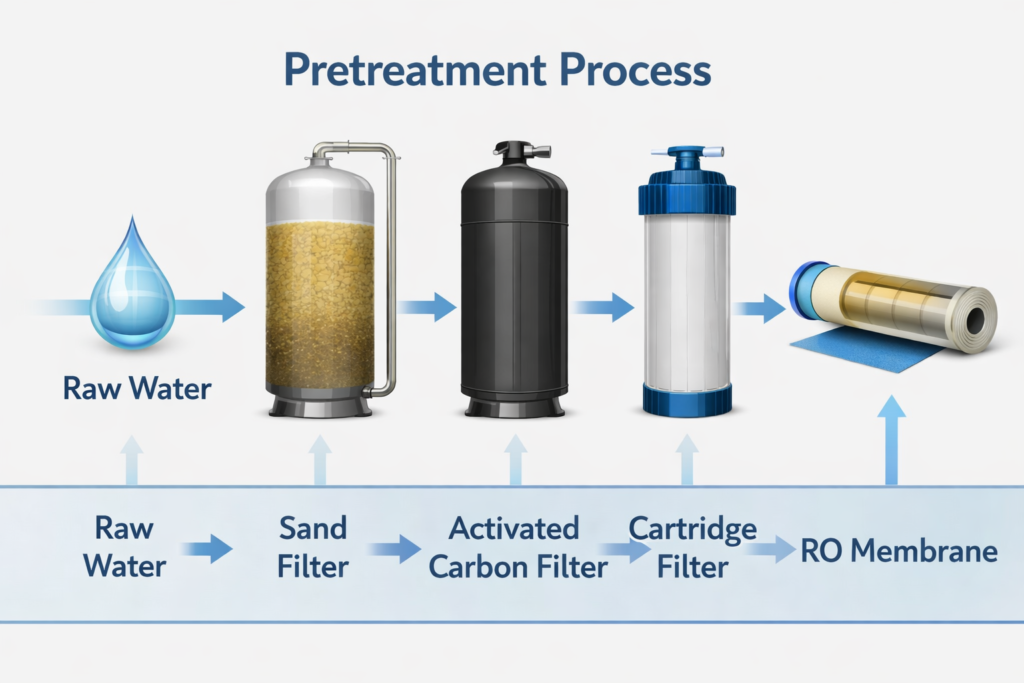
Inadequate pretreatment will allow contaminants to reach the RO membranes, accelerating fouling and reducing system performance.
Selection and Control of Pretreatment Chemicals
Pretreatment chemicals commonly include coagulants, flocculants, oxidizing agents, reducing agents, and antiscalants. Among these, the selection and dosage of coagulants and antiscalants have a particularly strong impact on RO membrane performance.
Improper chemical selection, overdosing, or incompatible formulations can lead to membrane fouling, organic contamination, and even irreversible membrane damage.
Aluminum Fouling Risks in RO Membranes and pH Control
In addition to iron, elevated aluminum concentrations in feed water can also cause serious RO membrane fouling. Aluminum fouling is mainly caused by the precipitation of aluminum hydroxide, which typically exists in colloidal form.
Aluminum hydroxide has very low solubility within a pH range of approximately 6.5 to 6.7. If coagulation occurs at excessively high or low pH values, dissolved aluminum may pass into the RO system and contaminate the membranes.
For pretreatment systems using aluminum-based coagulants, it is recommended to control the pH between 6.5 and 6.7, regularly adjust chemical dosage based on raw water quality, and monitor aluminum concentration after pretreatment. Ideally, aluminum levels should be maintained below 0.05 mg/L.
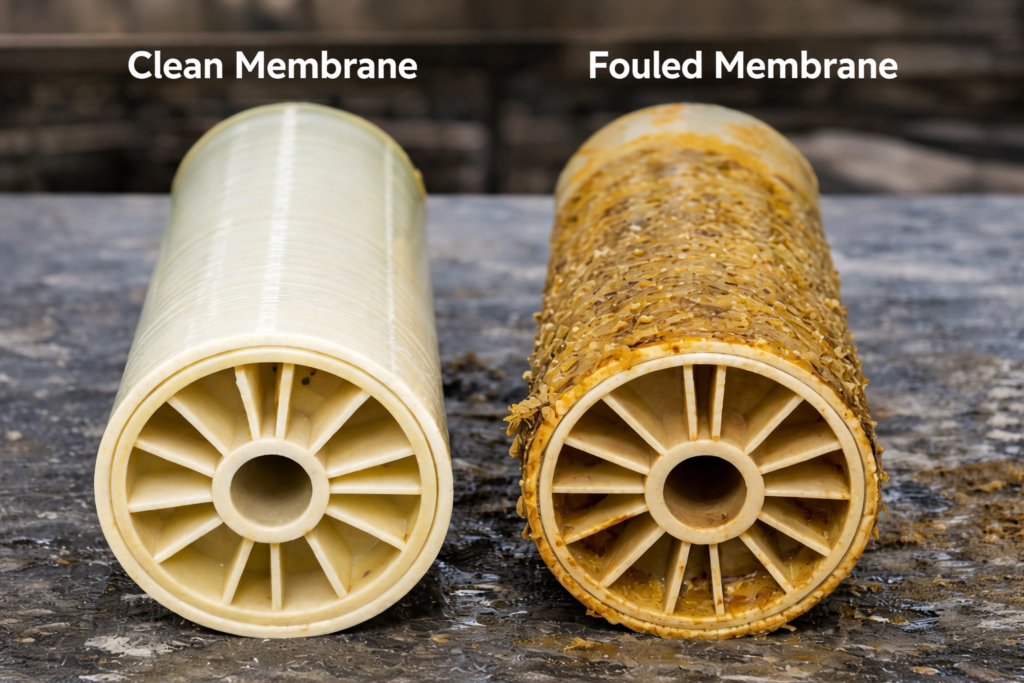

Potential Risks of Improper Antiscalant Application
Antiscalants are widely used to prevent scaling on the concentrate side of RO membranes. Most modern antiscalants are formulated from organic acids or organophosphates to provide scale inhibition and dispersion.
However, improper selection or poor dosage control may lead to organic fouling of the membrane surface. In some cases, antiscalants may also promote microbial growth, creating additional operational risks and reducing overall system durability.
Influence of Feed Water Temperature on RO System Performance and Durability
Effect of Temperature on RO Membrane Flux and Water Production
Feed water temperature has a significant impact on RO membrane flux and permeate flow rate. For this reason, temperature correction is required when comparing system performance under different operating conditions.
In cold regions, RO systems often experience reduced water production during winter. To maintain design capacity, some pretreatment systems incorporate heating equipment to stabilize feed water temperature and ensure consistent system output.
Silica Scaling Risks Under Low-Temperature Conditions
Silica scaling is closely related to feed water temperature. At approximately 25°C, the silica concentration in the concentrate stream should generally not exceed 100 mg/L, while at 5°C, the allowable concentration may drop to around 25 mg/L.
When no heating system is installed, special attention must be paid to silica scaling risks during winter operation. The silica concentration in the concentrate should always remain below its temperature-dependent solubility limit to prevent irreversible membrane fouling.
Why Operator Training Is Essential for Long-Term RO System Reliability
Operator skill level plays a critical role in reverse osmosis system durability. Well-trained operators can identify potential problems early and take corrective actions before serious damage occurs.
Incorrect operation, especially during system start-up and shutdown, may cause irreversible membrane damage. Proper flushing before and after operation is essential to prevent air entrainment, water hammer, and excessive salt concentration on the concentrate side of the membrane.
Standardized Operation and Maintenance Management for RO Systems
Routine Inspection and Replacement of Cartridge Filters
Cartridge filters should be inspected regularly and replaced in a timely manner to prevent particulate contamination of RO membranes.
When the differential pressure across the cartridge filter exceeds 0.15 MPa, the filter elements should be replaced. In general, cartridge filters should be inspected monthly, and the service life should not exceed six months.
During operation, it is also important to ensure that no air is trapped inside the filter housing.
Inspection and Maintenance of RO Membrane Elements
RO membrane elements should typically be inspected every six months, or more frequently if operating conditions require.
- Open pressure vessels using proper tools and qualified personnel
- Inspect the feed end for particulate deposits, metal oxides, and biological growth
- Check for changes in membrane color, scaling, or fouling
- If membranes are removed, always push them out in the direction of water flow
All inspection results should be recorded in detail to allow performance comparison and trend analysis over time.
Instrument Calibration and Operational Parameter Monitoring
Accurate instrumentation is essential for reliable RO system operation. Key operating parameters include operating pressure, recovery rate, SDI, pH, temperature, and residual chlorine.
Performance indicators such as salt rejection, permeate flow rate, and differential pressure must be continuously monitored. Operating limits should never be exceeded, as doing so may cause permanent membrane damage.
Operational Data Analysis for Early Problem Detection
Regular analysis of operating data helps identify abnormal trends at an early stage. By tracking changes in pressure drop, salt rejection, and water production, operators can take preventive actions before serious membrane fouling or damage occurs.
Conclusion: A Systematic Approach to Improving Reverse Osmosis System Durabilidade
Improving reverse osmosis system durability requires a systematic approach that integrates proper pretreatment, chemical control, temperature management, trained operators, and standardized maintenance procedures.
By focusing on long-term operational stability rather than short-term output gains, RO system operators can significantly extend membrane lifespan, reduce downtime, and achieve lower overall operating costs.
For additional technical references on reverse osmosis system design and operation principles, industry guidelines published by DuPont Water Solutions provide valuable insights into membrane performance and long-term system reliability.

